Trading in the financial market involves buying and selling financial instruments such as stocks, currencies, commodities, or cryptocurrencies to make a profit. Unlike investing, which focuses on long-term wealth accumulation, trading involves taking advantage of short—to medium-term price movements.
Traders use a variety of strategies and techniques to speculate on market trends and price fluctuations.
Understanding Different Trading Styles
Not all trading approaches suit every individual. The right trading style depends on multiple factors, including:
- Time Commitment: Some traders monitor the market throughout the day, while others prefer less frequent decision-making.
- Risk Tolerance: Different trading styles carry varying levels of risk, from short-term, high-risk strategies like scalping to more stable long-term approaches like position trading.
- Market Knowledge: Some styles require deep technical analysis, while others rely on fundamental factors or automated systems.
- Capital Availability: Higher-frequency trading may require larger capital due to margin requirements and transaction costs.
Understanding the different types of trading helps traders align their strategies with their financial goals, risk appetite, and market conditions.
Types of Trading Based on Timeframes
The choice of trading style often depends on the timeframe a trader prefers. Different timeframes come with distinct risk levels, required skills, and capital needs. Below are the four primary types of trading based on time horizons:
This type of trading can be broadly categorised into four types:
- Scalping
- Day Trading
- Swing Trading
- Position Trading
Scalping
Scalping is a high-speed trading style where traders aim to profit from small price movements within seconds or minutes. Scalpers execute multiple trades daily, often using leverage to amplify gains.
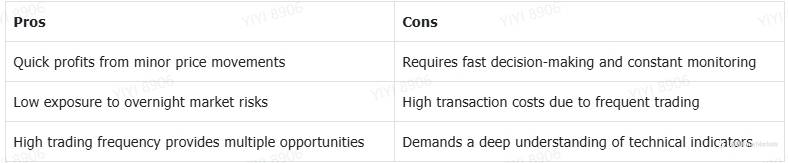
Scalping is most suitable for highly liquid markets, such as forex, stocks, and cryptocurrencies. Scalping strategies are primarily based on order flow analysis, moving average crossovers, and market depth tracking.
Scalpers use several technical indicators like Moving Averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands to open and close positions in the market. Such traders also often need Direct Market Access (DMA) and low-latency trading platforms.
Day Trading
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within a single trading day. Traders close all positions before the market closes to avoid overnight risk.
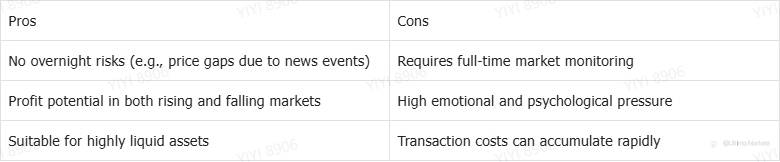
Day traders usually enter when the price moves beyond key support or resistance levels and follow strong price movements with high volume. These traders rely heavily on technical analysis and identify trend reversals using several indicators.
[H4] Swing Trading
Swing trading captures price swings over a few days to weeks. Traders aim to profit from short- to medium-term price movements rather than intraday fluctuations.

Swing trading suits assets with clear trends and liquidity, like stocks, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Some technical tools swing traders use are moving averages, Fibonacci retracements, and trendlines. Sometimes, swing traders also open positions based on fundamental analysis, including earnings reports, macroeconomic news, and interest rate decisions.
[H4] Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years. Unlike other trading styles, position traders focus more on fundamental analysis than short-term price fluctuations.

Position traders usually identify and follow macro trends to open and close trades. Such traders also heavily rely on buying undervalued assets based on fundamental analysis.
Each trading style suits different personalities, risk tolerances, and capital levels. The choice between them depends on an individual trader’s preference for time commitment, profit potential, and risk exposure.
Types of Trading Based on Strategies
Trading strategies differ based on how traders identify opportunities and execute trades. Some traders rely on trends, while others focus on range-bound movements or rapid price fluctuations.
The most common trading strategies are:
- Trend trading
- Range trading
- Breakout trading
- Momentum trading
- Arbitrage trading
- High-frequency trading (HFT)
Trend Trading
Trend trading involves identifying and following a prevailing market trend. Traders buy in an uptrend and sell in a downtrend, aiming to profit as long as the trend remains intact.
This type of trading is suitable for medium- to long-term traders (swing and position traders). Such traders require patience, as trends take time to develop, and they need to use technical indicators to confirm trends.
Some trend following indicators are:
- Moving Averages (MA): Helps smooth out price fluctuations and identify trend direction.
- Average Directional Index (ADX): Measures trend strength.
- Trendlines: Visual representation of price movements.
For risk management, trend traders use stop-loss orders below key support levels in an uptrend and above resistance in a downtrend. They also avoid entering trades late in a trend to prevent chasing prices.
Range Trading
Range trading identifies price ranges where an asset fluctuates between support and resistance levels. Traders buy at support and sell at resistance.
This type of trading is suitable for sideways (non-trending) markets and also works well in stable markets with no strong directional bias. Such trading also requires strict stop-loss management to avoid breakouts.
The key indicators for range trading are:
- Bollinger Bands: Helps identify overbought and oversold levels within a range.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Identifies potential reversal points.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Define the boundaries of the range.
Traders in range trading must be cautious, as false breakouts can trigger stop losses. Further, extended range-bound periods can lead to small, incremental gains rather than large profits.
Breakout Trading
Breakout trading involves entering a trade when the price moves outside a defined range, signalling the start of a new trend. Traders aim to capture strong price movements after a breakout.
Traders implementing breakout trading usually look for consolidation patterns like triangles, flags, or channels and observe increased trading volume to confirm the breakout. Bollinger Bands and Average True Range (ATR) are two widely used technical indicators in breakout trading.
Two key strategies in breakout trading are:
- Retest Strategy: Enter after the price pulls back to test the breakout level.
- Momentum Breakout: Enter as soon as the breakout occurs with strong volume.
However, traders must be cautious of false breakouts. Before entering, they must wait for a candle to close beyond a key level and use confirmation indicators like the RSI or MACD. They must also set a stop-loss below the breakout level to limit losses.
Momentum Trading
Momentum trading involves buying assets that show strong upward price movement and selling those that are losing strength. Traders ride the momentum until signs of reversal appear.
Momentum traders usually look for high trading volume as confirmation of strong moves, fast price acceleration in a particular direction, and continuation patterns that signal further strength.
The common indicators in momentum trading are:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Identifies overbought and oversold conditions.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Shows momentum shifts.
- Volume Indicators: Helps confirm the strength of a price move.
However, such trading strategies require rapid decision-making. There is also a high risk of reversals, which can lead to sudden losses.
Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage trading involves taking advantage of price differences between two or more markets for the same asset. Traders buy in one market and sell in another to profit from the price gap.
There are different types of arbitrage trading:
- Spatial Arbitrage: Buying an asset in one exchange and selling it on another at a higher price.
- Statistical Arbitrage: Using mathematical models to identify mispriced assets.
- Triangular Arbitrage: Exploiting price discrepancies between three related currency pairs.
Arbitrage trading can be very opportunistic as there is minimal risk involved. However, arbitrage opportunities exist for very short periods. Also, low-latency trading systems are required to execute arbitrage trades instantly.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
High-frequency trading uses algorithms and ultra-fast execution to profit from tiny price movements. HFT firms execute thousands of trades in milliseconds.
HFT trading is capital-intensive. It requires talent to design trading algorithms, high-speed data feeds, and low-latency connections.
Trade with Ultima Markets
Ultima Markets is a fully licensed broker and a multi-asset trading platform offering access to
250+ CFD financial instruments, including Forex, Commodities, Indices and Shares. We
guarantee tight spreads and fast execution. Until now, we have served clients from 172
countries and regions with our trustworthy services and well-built trading systems.
Ultima Markets has achieved remarkable recognition in 2024, winning prestigious awards
such as the Best Affiliates Brokerage, Best Fund Safety in Global Forex Awards, and
the Best APAC CFD broker in Traders Fair 2024 Hong Kong. As the first CFD broker to join
the United Nations Global Compact, Ultima Markets underscores its commitment to
sustainability and the mission to advance ethical financial services and contribute to a
sustainable future.
Ultima Markets is a member of The Financial Commission, an international independent
body responsible for resolving disputes in the Forex and CFD markets.
All clients of Ultima Markets are protected under insurance coverage provided by Willis
Towers Watson (WTW), a global insurance brokerage established in 1828, with claims
eligibility up to US$1,000,000 per account.
Open an account with Ultima Markets to start your index CFDs trading journey.
风险提示:以上内容仅代表作者或嘉宾的观点,不代表 FOLLOWME 的任何观点及立场,且不代表 FOLLOWME 同意其说法或描述,也不构成任何投资建议。对于访问者根据 FOLLOWME 社区提供的信息所做出的一切行为,除非另有明确的书面承诺文件,否则本社区不承担任何形式的责任。
FOLLOWME 交易社区网址: www.followme.ceo


加载失败()